Marketing an eCommerce store feels like shouting over a packed stadium crowd. In 2025, there are nearly 12 million eCommerce websites in the US alone. That’s 3x more than in 2019. Even in very niche verticals, you’re competing against thousands of merchants.
With so many businesses vying for customer attention, your product pages need excellent SEO optimization to stand a chance of ranking on the first page. In this guide, you will learn how to improve SEO for eCommerce product pages. We will also share some SEO for eCommerce best practices and answer a few frequently asked questions.
9-Step eCommerce Product Page SEO Optimization Process
Let us show you how to optimize your product pages for increased visibility in search results in nine (mostly) simple steps.
1. Prioritize Most Wanted Products
Even if your eCommerce website isn’t massive, you can’t optimize all your product pages — not at once. So start by identifying products in high demand among your customers.
Here’s how to do it with Doofinder analytics tools: Head over to the Search Stats in your Admin Panel and scroll down to the section with the Top Clicked chart. That’s the list of products customers clicked on the most. These are the product pages you should optimize first.
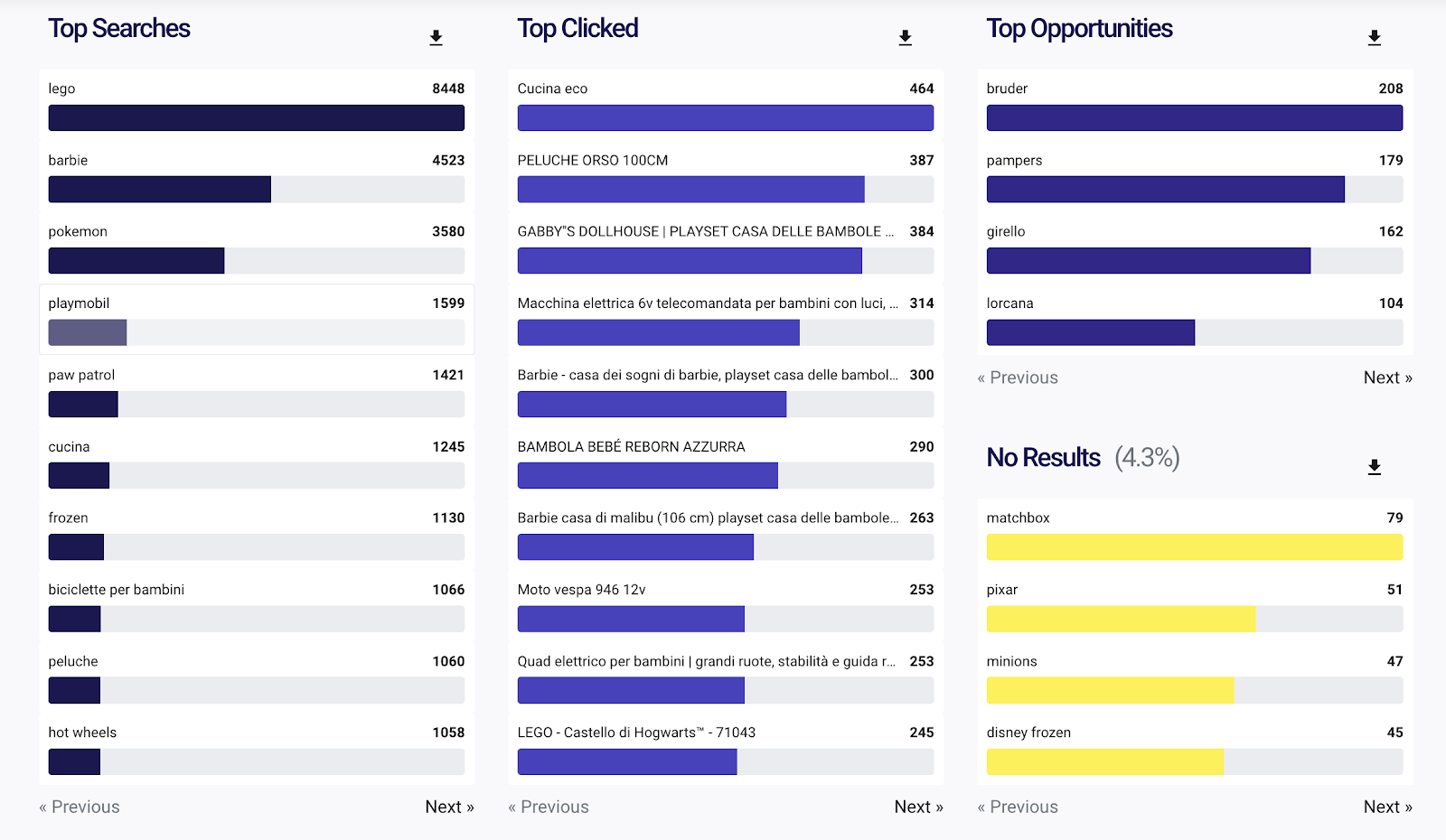
What if the demand for your products fluctuates throughout the year? From the search data above, you can see that lego and barbie are the most searched for terms in this particular shop overall.
However, interest in them is might drop as we head into summer. To find pages that are your priority at the moment, filter the search data by date.
Editor’s note: Top clicks and internal search volume aren’t the only metrics you can use. Others include click-through rates, sales volume, profit margin, and total profit per product.
2. Conduct Keyword Research
When you click on the product bar, Doofinder provides data on the specific queries used by your store visitors to search for them.
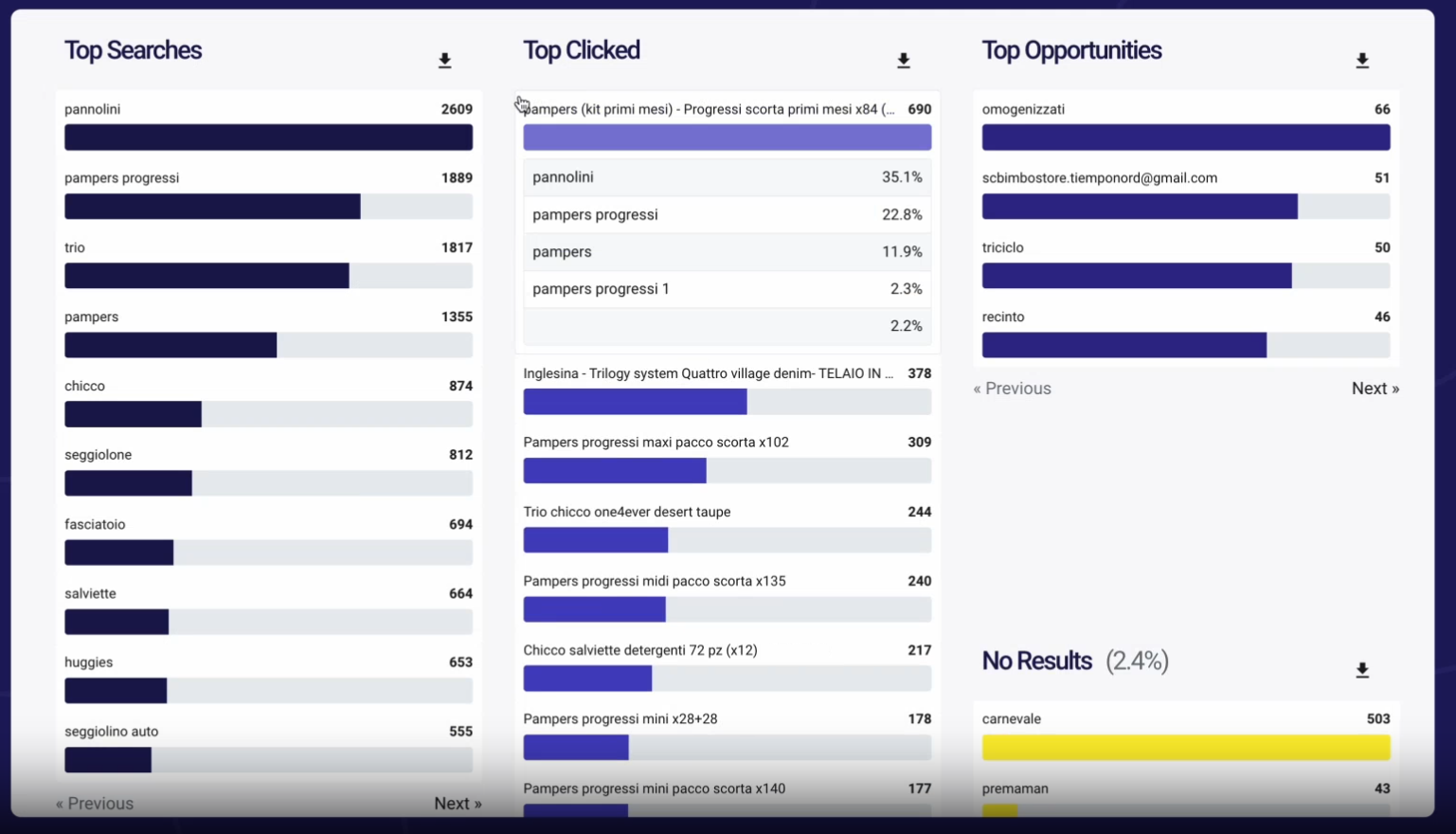
The challenge is that customers may not always use the same keywords when searching for the product on Google. You can find them in Google Search Console by analyzing the Queries for a particular page in the Performance report.
However, this only shows you what keywords your page already ranks for, not ones that you should optimize it for to improve their performance. To find these, you need different tactics. And different tools.
Use Ahrefs to Identify the Keywords Your Competitors Rank For
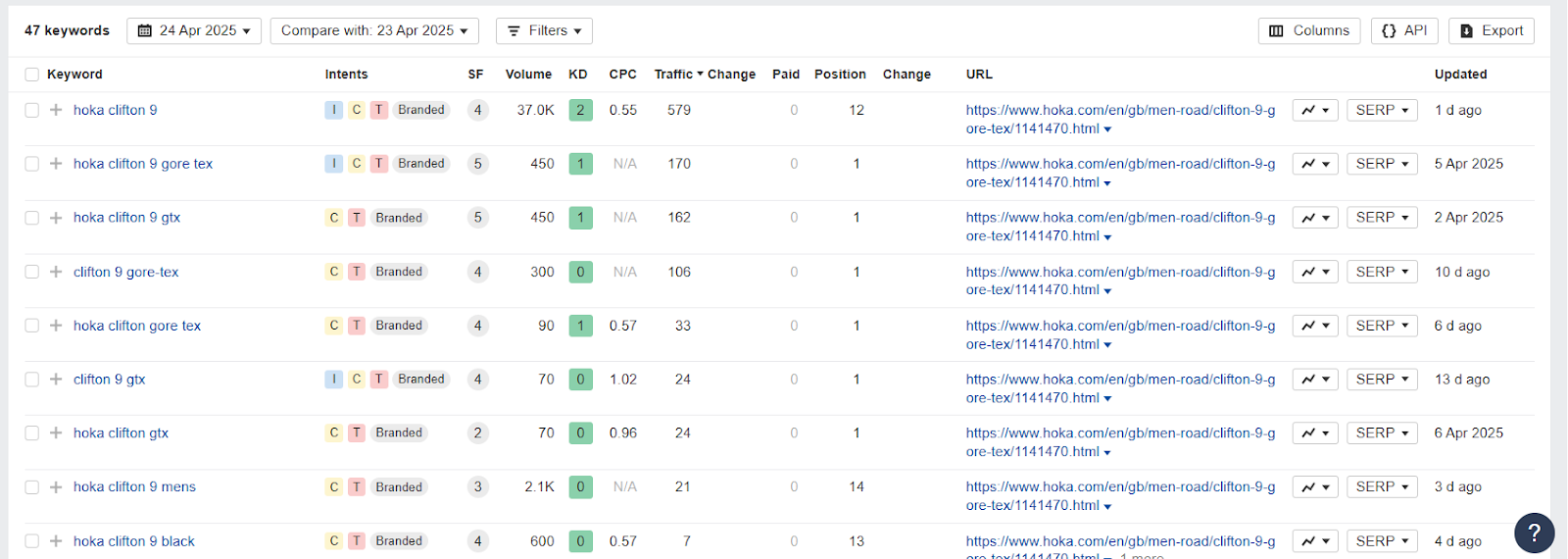
Let’s imagine your best-selling product is a running shoe, the men’s version of Hoka Clifton 9 with the Gore-Tex membrane.
- Search for “hoka clifton 9 gore tex for men” in Google to identify your key competitors.
- Pick eCommerce websites from the search results. In this particular case, Hoka holds the number 1 spot (surprise, surprise).
- Plug the product page into Ahrefs Site Explorer and head to the Organic Keywords report.
- Filter the results to include only those with transactional intent.
That’s how you get a list of the top organic keywords the page ranks for. These are the keywords you want to optimize your product page for.
💡 Pro tip: You can use this tactic to identify all keywords your main competitor ranks for and then map them to your product categories and product pages. Instead of searching for a specific product page, plug the category page or the entire shop URL into the search bar.
Use Content Optimization Tools
Once you identify your primary and secondary keywords, use a content optimization tool like Surfer, Clearscope, or NeuronWriter to brainstorm other keywords you may want to include on your product page.
- Enter the keyword you want to rank for.
- Select the pages you want to compete against to customize the suggestions.
- Select relevant keywords to incorporate into your product page content.
3. Optimize Product Page Titles, Meta Titles, and Meta Descriptions to Attract Clicks
The next step is to optimize your product page titles (H1s), meta titles, and meta descriptions.
A product page title is what users see when they visit the product page, and the meta title is what they see when the page appears in the search results.
They are usually the same and normally include a combination of product kind, brand name, product series name, model name, features, variant, SKU number/product code, etc.
For example, Walmart TV page titles consist of
- Brand name (onn.),
- Screen size (50″),
- Display resolution (Class 4K UHD (2160P)),
- Screen technology (LED),
- Smart TV platform (ROKU),
- HDR
- Model number (100012585)
How do you choose the right combination?
Use your keyword research insights. But look at the keywords at the category page level, not at the product page level.
You want a consistent title structure across all products in the same category, and by using only one product as a reference, you may omit important keywords similar products rank for.
Meta description is the short text snippet, up to 156 characters, that appears in SERPs below the product page title/meta tag. While meta descriptions don’t directly influence rankings in search, they can improve click-through rates (CTRs).
At least, that’s what SEOs believed for a long time. However, there’s evidence that their optimization has no impact on traffic. This is partly because Google rewrites up to 75% of meta descriptions to better serve user queries.
4. Write Unique, Value-Focused Product Descriptions
Many e-commerce businesses copy the manufacturer’s product descriptions and call it a day. We can understand why this happens: they have hundreds, if not thousands, of product pages to create and limited resources. But it’s a missed opportunity. A unique product description is your chance to stand out from competitors. And to convince your customers to buy.
How do you write compelling product descriptions?
- Focus on product benefits and use cases, not features. Tell your prospective customers how the product will improve their lives.
- Use sensory and emotional language and narratives.
- Provide all the product data necessary to make an informed decision. For example, a size chart for shoes or clothing.
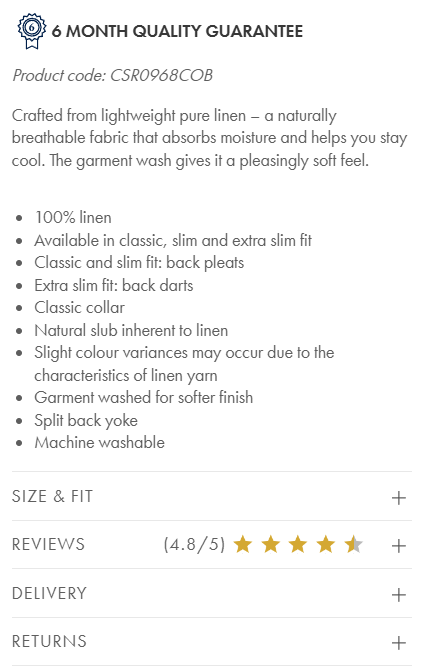
Here’s a great example from Marks & Spencer. Its linen shirt description connects the product features with its benefits (the “breathable fabric…helps you stay cool”) and uses sensory language (“pleasingly soft feel”). Your product descriptions can also improve your rankings, so include relevant keywords. Like “pure linen” and “100% linen” in the below example.
Use keywords to communicate, not to play the algorithms. That’s keyword stuffing, and it’s against Google’s spam policies. It can harm SEO performance.
5. Use Headings to Organize The Product Page
Breaking down your product page into sections with relevant headings helps readers and search engines understand the page content.
H1 heading is product title, so that’s already sorted.
H2 headings are normally for main page sections, like “Product details” or “Size & Fit”, and H3 headings for specific features and benefits.
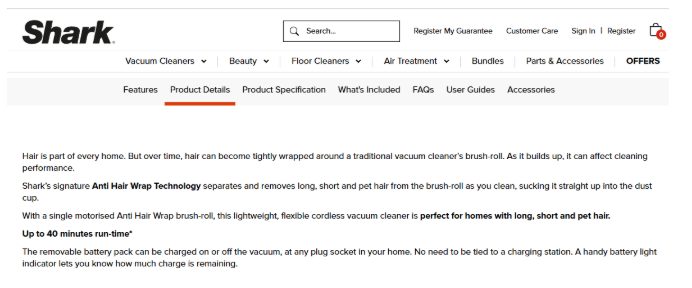
Shark, the vacuum cleaner manufacturer, divides its product page into 6 H2 sections (Features, Product details, etc.) and then breaks them down into H3 sections focusing on specific features (Up to 40 minutes run-time, two floor modes, etc.)
Pro tip: Write descriptive headings and use bullet points to make your product description scannable and skimmable. It helps the reader get a quick overview of what the product offers and find the relevant information.
6. Structure URLs with Clarity and Embed Keywords
Product page URL optimization comes next.
Readable, keyword-rich URLs help search engines and users understand what the page is about. They also help customers navigate your website and share pages.
Here are a few tips:
- Create a logical site structure: category/subcategory/page, for example, /coffee-machines/espresso/delonghi-dedica-espresso-machine/
- Keep them concise and tidy. Don’t include unnecessary parameters or dates.
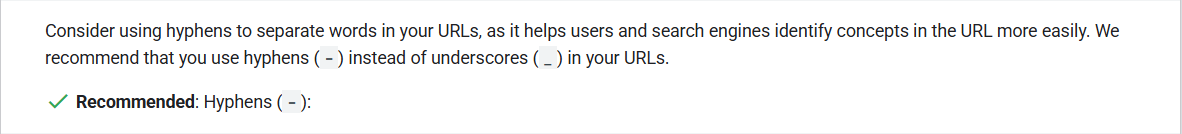
Use hyphens instead of underscores to make them easier to read (for users and Google.)
7. Add High-Quality Product Images and Videos
Did you know? According to MagePomp, 30% of all online shopping experiences in 2023 involved visual search. Customers see a picture of a product that they like, but they don’t know its name, so they use Google Lens to find it.
So, quality images improve your product discoverability.
There’s more! Visuals, especially videos, increase user engagement on the page, leading to higher dwell times, which Google uses as a ranking signal.
When it comes to image SEO optimization, here are a few tips:
- Compress images into the WebP format to improve page speed.
- Host the images on your domain, not on third-party services. For better performance and to drive traffic to your site.
- Use <img src> instead of CSS to embed images. This helps Google index them.
- Use descriptive file names and alt tags for SEO and accessibility. Include your domain, product name, type of product, color and/or size, and main features.
8. Improve Internal Linking to Support Crawling and Authority Flow
Optimizing your product page copy and visuals isn’t enough. To rank, pages need backlinks. The more backlinks from established websites point to your product page, the more trustworthy it is in Google’s eyes.
The challenge? Building links to individual product pages isn’t always feasible. Even if you have only several dozen of them, it takes a lot of time and money. And if your inventory changes a lot, you will never keep up.
But there’s a solution:
Build links to category pages and other more linkable resources, like your blog posts, and funnel the PageRank, or link juice, to your product pages via internal links.
On the product page, provide links to:
- Category pages
- Alternative products
- Related products frequently bought together
- Relevant complementary pages, for example, guides on how to use the product.
Don’t forget to link back to your product page from other relevant pages on your site. For example, update your blog posts to mention the product or include sitewide links if it’s a major product.
Editor’s note: Internal links also improve page indexation and product discoverability.
9. Improve User Experience
Another factor that will give your product page an edge over equally well-optimized competitors is an excellent user experience. The Google API leak in 2024 confirmed that Google considers user behavior signals, like bounce rate and dwell time, to rank pages.
Simply put, if a user clicks on a page and spends time on it, it’s a signal that it satisfies their expectations, and Google promotes it. If, on the other hand, they click on a page and return to the SERP immediately, it means it doesn’t give them what they need.
So, how do you optimize your eCommerce website for an excellent user experience?
- Use CDNs, compress images and videos, and leverage browser caching to improve the page loading times.
- Place critical product information, such as name, price, and images, above the fold to immediately capture customer attention.
- Use white space, large fonts, bolded and italicized text, and bullet points to create a clear page layout and help users find what they need.
- Provide breadcrumbs to improve website navigation.
- Remove unnecessary steps from the checkout process. Include the “Buy now” button and enable single sign-on (SSO) so they can create an account with their existing social media or email credentials.
- Provide accurate search results. Doofinder uses AI to analyze customer queries to serve them the most relevant results.
eCommerce Product Page Optimization Best Practices
The 9-step process above is a high-level framework.
Let’s unpack nine product page optimization best practices to supplement it and help you maximize your product page potential.
1. Provide Relevant Product Recommendations to Keep Customers Engaged (and Sell More)
Businesses that offer product recommendations on their product pages sell more. According to Barilliance, almost a third of eCommerce business revenue comes from product recommendations.
However, not all recommendations are relevant. The fact that I’ve just bought a washing machine doesn’t mean I’m interested in another one. You can improve product recommendation relevance with Doofinder AI-powered recommendations. In essence, we use customer behavior data to recommend complementary products that customers truly need.
2. Optimize Your Page for Mobile Devices
Your potential customers are likely to be mobile phone users. You’ve seen the stats. Semrush 2023 data shows that mobile users bring 4x more traffic. Statista estimates that around 80% of all eCommerce website visits in 2024 came from mobile devices, and mobile sales accounted for 70% of all eCommerce transactions.
With that in mind, optimize your eCommerce product pages for mobile devices.
Here’s how:
- Use responsive design to make sure the page looks good on all device types.
- Optimize page loading times. Mobile users have lower tolerance for slow-loading pages and bounce sooner.
- Provide mobile-friendly navigation with clear icons, touch-friendly buttons, intuitive menus, and swipe nav for images.
- Use images that clearly display your product on small screens.
- Use larger text, concise content, and shorter H2/H3 sections.
3. Add Interactive Elements to Keep Users on the Page
Adding interactive elements to your page is another way to improve user experience and boost dwell times on your pages.
These could be:
- Interactive size guides. For example, the size guide by BananaFingers helps you choose the right climbing shoe size based on your existing or street shoe size.
- Virtual try-ons. For instance, with Specsavers Virtual Try-On, you can “try on” glasses before ordering.
- Augmented reality experiences. If you’re buying furniture from Ikea, you can see how it fits into your room.
- Product comparison tables. For instance, in Carwow, you can create custom car comparison tables.
- Calculators, for example, tile calculators, like the one from gotiles.com.
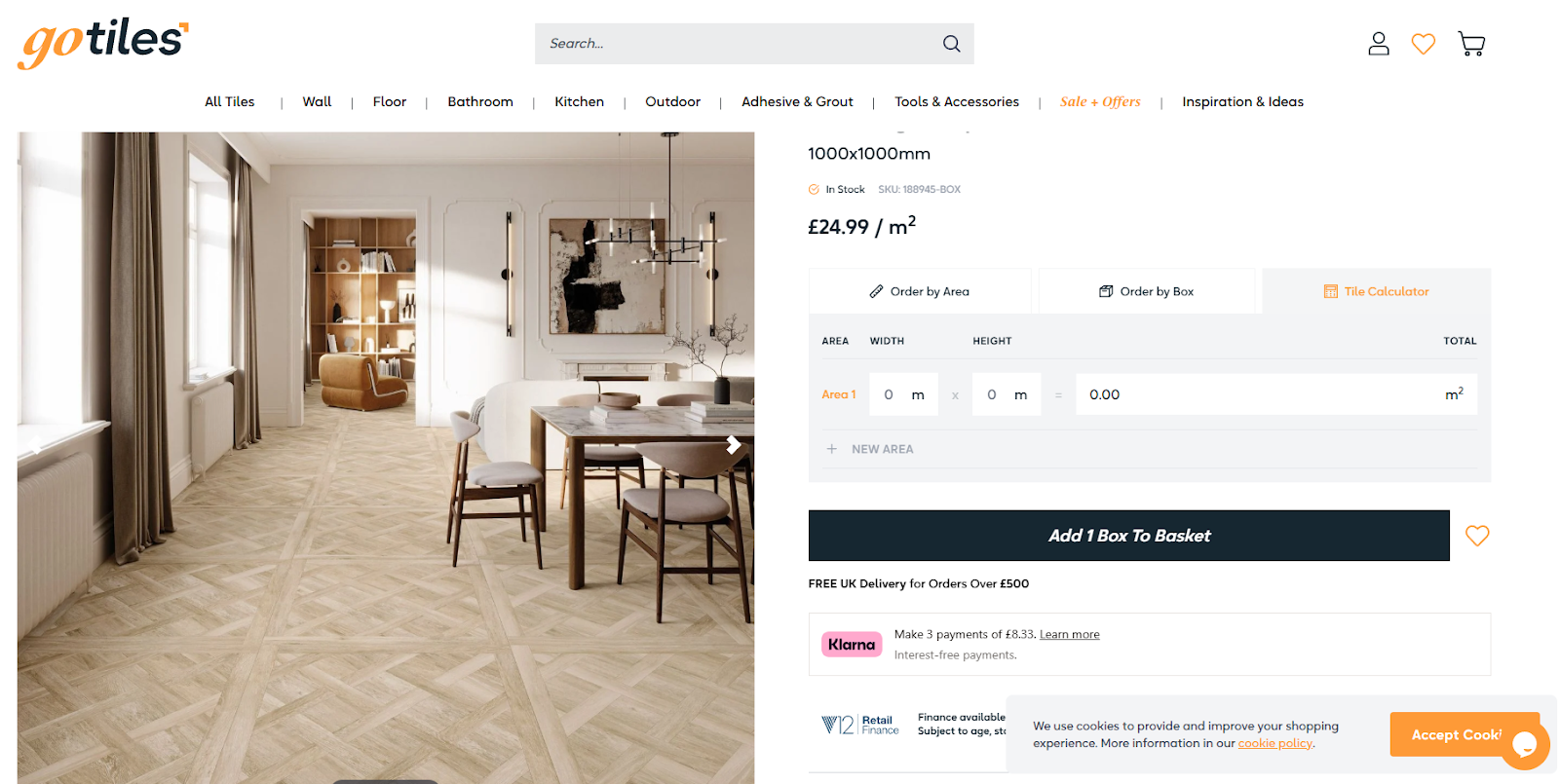
4. Implement Structured Data for Rich Results
Schema markup and structured data help Google understand page content.
More importantly, they help your product stand out in SERPs through rich snippets and rich results, leading to higher CTRs.
Here’s an example.
The Hoka search result features:
- A breadcrumb
- An image
- Price
- Availability (In stock)
- Customer rating
- Delivery and returns details.
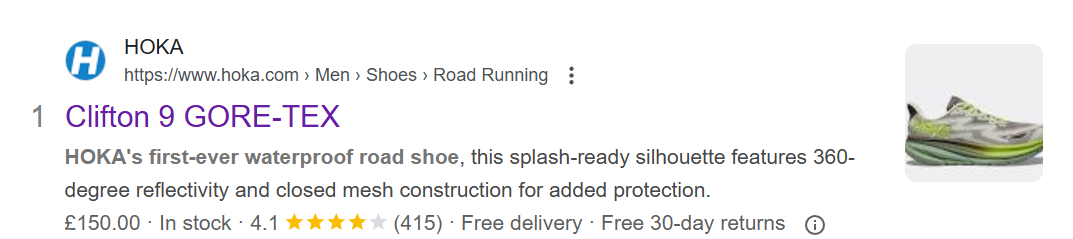
This result is more likely to capture customer attention than one made of the product name and meta description only.
What kinds of Schema types can you use?
- Product schema (name, description, price, availability, offers, seller info, etc.)
- Review and aggregate rating schema
- Breadcrumb schema
- HowTo schema
- Video schema
- FAQ schema
5. Answer Common Customer Questions in the FAQ Section
By answering common customer questions it makes your product description more comprehensive, which can improve conversions. Fewer unanswered questions about a product leads to more purchases.
They’re also an opportunity to embed more related keywords, and your responses can get featured in the People Also Ask section, increasing visibility.
How do you choose relevant questions to answer? Extract them from past customer enquiries and supplement with keyword research data.
6. Display User-Generated Content to Add Authenticity
Have you ever purchased a product, impatiently waited for its delivery, just to discover that it looks very different from what you expected? We’ve all been there.
Your potential customers, too, and that’s why they may be cautious with their purchases. To dispel customer concerns, more and more e-commerce product pages feature user-generated content. Think: images, videos, and reviews.

And it works. Data shows that just a few reviews can increase conversions by 52.2%, and 56% of consumers are more likely to buy a product if they see it in a UGC photo.
7. Localize the Pages for International Audiences
If your product pages target different locations around the globe, localize them. This involves more than translating the pages into the target language:
- Customizing pages culturally. For example, use product images featuring local models.
- Adjusting your pricing for local markets.
- Accommodating local payment methods, for example, Blik in Poland and WeChat Pay in China, instead of PayPal.
- Building links from pages in the target GEO locations to increase your page relevance and bring referral traffic.
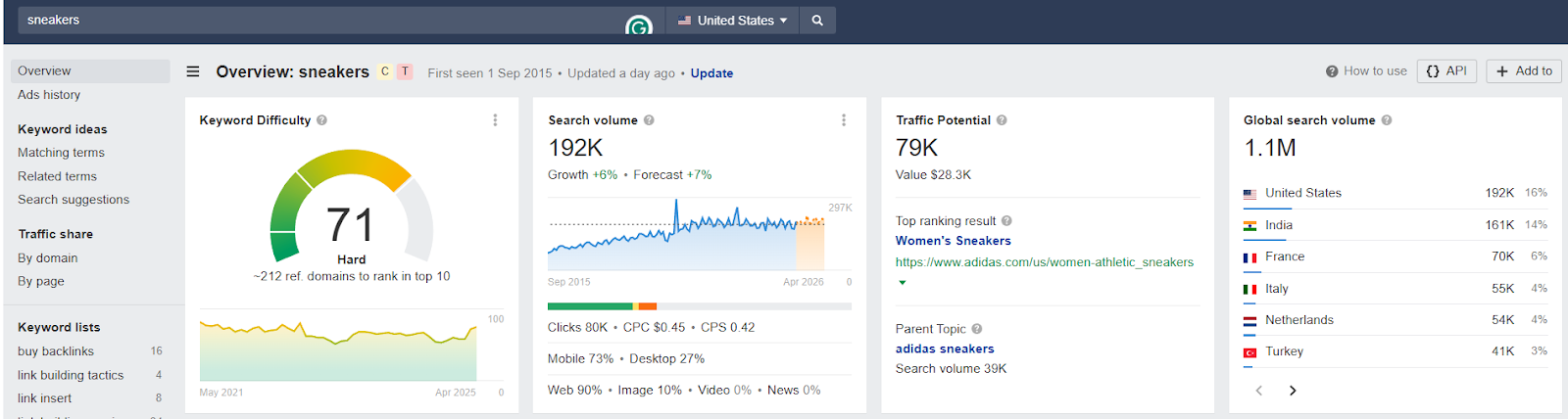
Targeting region-specific keywords. For example, if you’re in the running shoe business, keyword “sneakers” has a much greater traffic potential in the US than “trainers” which you’d target in the UK.
8. Improve Crawling and Indexing with XML sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a document that tells the search engine what pages exist on your domain and how they’re linked to each other. By keeping them up-to-date, you help search engine bots crawl your website and discover new pages.
If you manage a large website, consider using different XML sitemaps for different page types, for example, category pages, product pages, blog posts, etc. It makes it easier to update them, diagnose issues, and gives you more control over which pages are crawled and when.
💡Pro tip: Use the <lastmod> and <changefreq> attributes to help Google find changes and save your crawl budget.
9. Use Analytics Tools to Measure Performance and Iterate
Product page SEO optimization is an ongoing process. Even if you nail it first time round (unlikely), consumer behavior changes over time, and what worked yesterday may not work tomorrow.
This means constantly measuring their performance and iterating on the insights. Here are a few ideas:
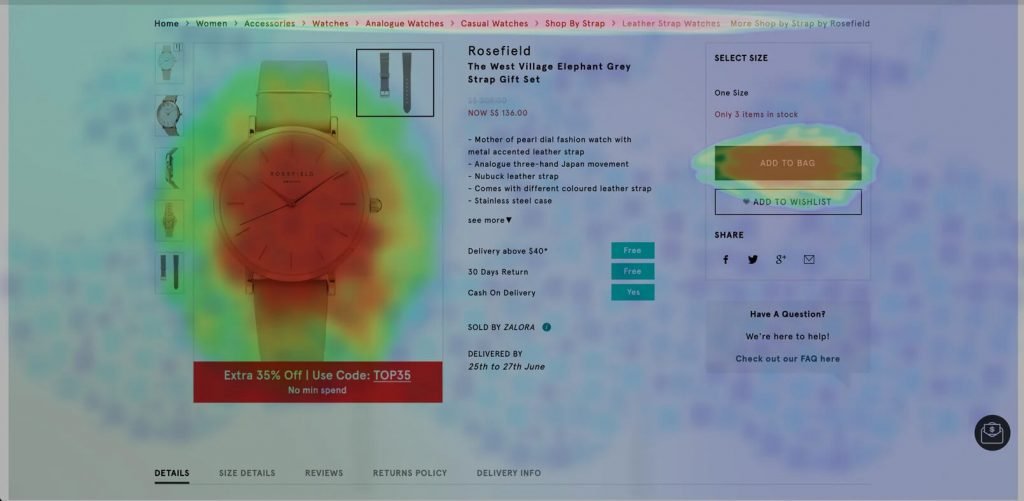
- Analyze heatmaps and session recordings to understand user interactions with the page, for example, how far they scroll or where they click.
- Track keyword performance in Ahrefs and/or Google Search Console to identify shifts in user search behavior.
- Run A/B tests to choose the best-performing titles, descriptions, and page designs.
- Leverage Google Analytics 4 to track traffic sources, bounce rates, and conversion paths on your site.
- Use Doofinder to keep track of CTRs and conversion rates on your page.
Conclusion
Great product page SEO requires a combination of on-page optimization, technical SEO, and user experience optimization.
What’s next for you? Start by auditing your page to assess its performance (this will be your benchmark) and identify pages to optimize first. Then, proceed with keyword research and optimize each aspect of performance using the 9-step process outlined above.
If you’d like to see how Doofinder can improve your eCommerce performance, start your free trial today!
SEO for eCommerce Product Pages FAQs
If your product is out of stock, inform the customer and suggest alternative products. If you’re expecting a new batch, let them know the ETA.
If the product is discontinued, you have three options:
- Use the same URL for the new product version. But only if the differences between the two versions are marginal.
- If there’s no new version but the page gets lots of traffic, keep it. Inform the visitors that the product is no longer available and suggest alternatives.
- If there’s no new version and it’s a low-demand page, redirect it to a category page (and, again, explain why this is happening).
If you have separate product pages for different variants, for example, sizes or colors, there’s a risk of keyword cannibalisation. That’s when nearly identical pages on a website compete for the same traffic.
To avoid diluting the ranking signals across multiple pages, SEOs do two things.
One is consolidating all variant pages into a single page with internal selectors for colors, sizes, models, etc.
The other approach is to choose the page that gets the most organic traffic and canonicalize the other versions to it. Canonical tags tell Google that these are variants, not independent pages, and direct crawlers to the main page.
Alternatively, you can remove the variant pages from search altogether by adding the noindex tag.
Fresh content ranks higher because it generally serves customers better. However, there are no hard-and-fast rules on how often you should update product pages.
The update frequency depends on factors like:
- Product changes: When the product evolves, for example, gets new features, the page needs to reflect it.
- Traffic drops: If you notice a dip in traffic, update the page to realign it with the search intent. For example, by optimizing it for different keywords.